China’s Floating Solar Farms: 7 Key Facts Driving a Sustainable Future
Introduction
Solar power is no longer limited to land. In a groundbreaking move, China has built massive floating solar farms on water, revolutionizing how renewable energy is generated. This innovative approach helps preserve farmland for agriculture while producing clean electricity at scale. A recent viral X (formerly Twitter) post by @gunsnrosesgirl3 showcased an extraordinary video of one such floating solar installation, sparking global conversations about the future of sustainable energy.
The Viral X Post and Video Breakdown
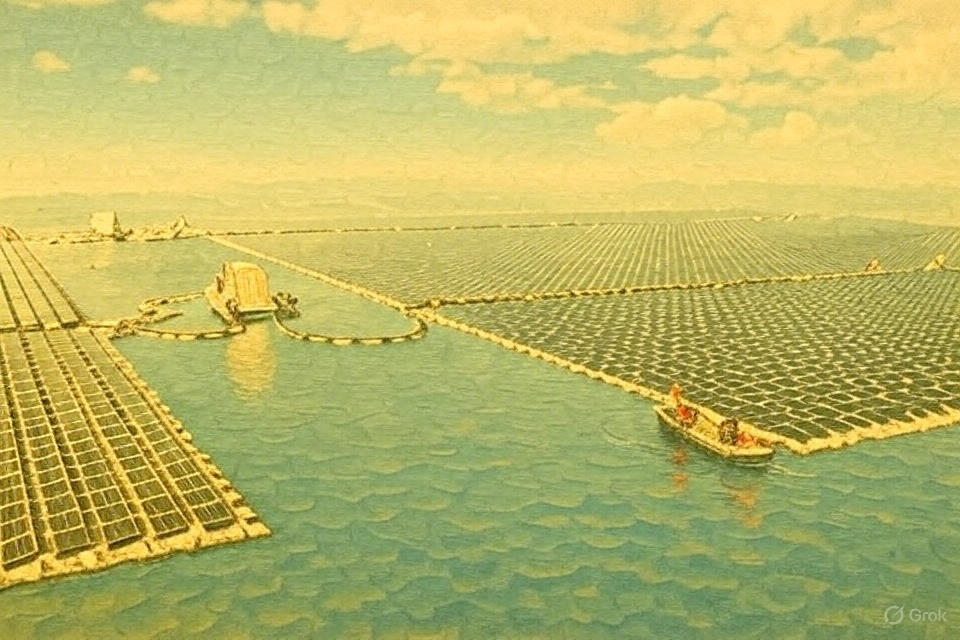
On October 2, 2025 (06:30 AM IST), @gunsnrosesgirl3 shared a 16-second video offering a breathtaking aerial view of China’s floating solar farm.
China is putting enormous solar farms on water because they want to use land for agriculture
— Science girl (@gunsnrosesgirl3) October 2, 2025
pic.twitter.com/r0kPknX3Br
Video Timeline Highlights:
- 0–5 seconds: Wide aerial shot showing a vast grid of solar panels floating on a brownish waterbody.
- 5–10 seconds: A closer look at the floating HDPE platforms supporting the solar panels.
- 10–15 seconds: The panels’ reflective surfaces highlight their seamless integration with the water below.
- 15–16 seconds: Side view reveals the raised platform structure that minimizes land use while optimizing solar exposure.
“China is putting enormous solar farms on water because they want to use land for agriculture.”
This simple statement underscores the key motivation — optimizing land use for both energy and food production.
Why Floating Solar Farms Matter
Floating solar farms (also called FPV – Floating Photovoltaic) are reshaping the future of energy production. China, the world leader in renewable energy investments, is leveraging water surfaces to meet its green energy goals.
7 Key Facts About China’s Floating Solar Farms
- Land Preservation: Shifting solar panels to water frees up valuable agricultural land.
- Higher Efficiency: Water’s cooling effect can improve panel performance by up to 15%.
- Water Conservation: Covering reservoirs reduces evaporation, helping in drought-prone areas.
- Climate Impact: Contributes significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Engineering Scale: Some farms in China cover over 1,000 acres of water surface.
- Environmental Challenges: Shading water bodies may disrupt aquatic ecosystems.
- Global Benchmark: China’s rapid deployment sets a model for other nations adopting FPV technology.
Benefits vs. Challenges
| Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Preserves farmland | Potential aquatic ecosystem disruption |
| Boosts panel efficiency via cooling | Maintenance in harsh weather (storms, winds) |
| Reduces water evaporation | Possible chemical runoff from panel cleaning |
| Supports national clean energy goals | Higher initial installation costs |
Global Context
Floating solar is not just a Chinese innovation. Countries like Japan, Israel, India, the UK, and Singapore are also experimenting with FPV projects. By 2023, the global solar capacity had crossed 1,200 GW, with floating systems contributing an increasing share. China’s large-scale projects, however, have set the global benchmark for combining renewable energy with strategic land management.
FAQs
Q1: Why is China focusing on floating solar farms?
A: To maximize land use — preserving farmland for food production while expanding clean energy generation.
Q2: Are floating solar panels more efficient than land-based ones?
A: Yes. Cooling from the water can improve efficiency by up to 10–15%.
Q3: Do floating solar farms harm the environment?
A: While they help reduce emissions and water loss, they may impact aquatic ecosystems and need careful management.
Q4: How much energy can these farms produce?
A: Large-scale floating solar projects can generate hundreds of megawatts (MW), powering thousands of homes.
Q5: Is floating solar the future of renewable energy?
A: It’s a key part of a diversified clean-energy strategy, especially for countries with limited land availability.
Conclusion
The viral X post by @gunsnrosesgirl3 reveals more than just a stunning visual — it highlights a paradigm shift in renewable energy strategy. Floating solar farms demonstrate how innovation can solve multiple problems at once: energy production, land conservation, and climate mitigation.
As global energy demand grows and climate challenges intensify, the success of China’s floating solar farms could inspire a worldwide transition toward water-based energy solutions.
Opinion
The rise of floating solar technology raises profound questions for society, governments, and energy planners. While the environmental benefits are clear, the ethical and ecological trade-offs remain complex. Should human innovation prioritize immediate climate gains even if it alters aquatic ecosystems? Can countries with fewer water resources replicate China’s model without unintended consequences?
These questions highlight a central tension in our transition to green energy: progress versus preservation. China’s floating solar farms symbolize both the promise and the dilemma of modern sustainability — they demonstrate our capacity for bold solutions but also remind us that each technological leap reshapes our planet in ways we are only beginning to understand.
This debate challenges policymakers and ordinary citizens alike to think critically about how to balance technological progress, environmental integrity, and social equity. The story of floating solar is, ultimately, not just about panels on water — it’s about humanity’s evolving relationship with the natural world.

0 comments